The Ultimate Guide to Studying in Canada: Why It's the Right Choice

Canada has quickly become a top destination for international students—and the numbers prove it. In 2023 alone, over 1,040,000 international students were enrolled across all education levels, marking a 29% increase from the previous year and a 250% surge over the past decade. Students from around the world see Canada as a hub for academic excellence and career opportunities. Among them, India leads with 41%, followed by China (10%), the Philippines (5%), and countries like Nigeria, France, Iran, Mexico, and Brazil, each contributing more than 2%.
Diverse Student Population
A major advantage of studying in Canada is its vibrant, multicultural student community. Learners from every continent bring unique perspectives, creating a global classroom. Currently, 41% of international students come from India, while China, the Philippines, Nigeria, France, Iran, and Mexico also make significant contributions. This diversity ensures a rich cultural exchange and an inclusive academic atmosphere.
Safe and Stable Environment
Canada consistently ranks among the safest countries in the world, making it a reassuring choice for students and their families. Whether you live in a lively city or a smaller town, Canada provides a secure environment with a strong emphasis on community well-being.
High-Quality Education
Home to some of the world’s leading universities, Canada’s education system is globally respected. Ten Canadian universities, including the University of Toronto, the University of British Columbia, McGill University, the University of Alberta, and the University of Waterloo, rank among the top 150 worldwide. This means that students graduate with qualifications that are highly valued by employers and institutions worldwide.
Inclusive and Tolerant Society
Canada is known for its diverse and welcoming culture. Students from different religions, ethnicities, and cultures are embraced and supported. This ethos extends beyond campus life, offering international students a truly enriching and inclusive experience
Pathway to Permanent Residence
One of the most attractive benefits of studying in Canada is the clear pathway to permanent residency (PR). With programs like the Post-Graduation Work Permit (PGWP), international students can stay and work in Canada for up to three years after graduation. This work experience not only builds careers but also provides eligibility for PR under various immigration programs.
The Canadian Education System
Canada’s education system is built on strong academic standards and innovation. With more than 100 universities, including globally recognized institutions such as the University of Toronto and McGill University, students have access to diverse programs and research opportunities.
Study Permit and Visa Requirements
To study in Canada, international students must secure a study permit (and in some cases, a visa). This requires:
- An acceptance letter from a Designated Learning Institution (DLI)
- Proof of financial resources
- Supporting documents specific to your country of residence
Checking eligibility early ensures a smooth transition into your studies.
Designated Learning Institutions (DLIs)
Not all colleges and universities are authorized to host international students. Only DLIs are eligible. All primary and secondary schools qualify as DLIs, but at the post-secondary level, students must confirm their chosen institution is on the government-approved list.
Choosing the Right College or University
When selecting a Canadian institution, factors to consider include:
- Program offerings and career relevance
- Campus location and lifestyle
- Facilities and support services
- Reputation and global ranking
Top choices include the University of Toronto, McGill University, University of British Columbia, Université de Montréal, and McMaster University
Language Proficiency Requirements
Most institutions require proof of English or French proficiency, depending on the program’s language of instruction. Accepted tests include IELTS, TOEFL, and PTE Academic. In some cases, additional language courses may be required after enrollment.
Scholarships and Financial Aid
Financing education is often a major concern, but Canada offers a wide range of scholarships, grants, and bursaries for international students. These may be awarded based on academic achievement, extracurricular involvement, or criteria tied to a student’s home country or program of study. Scholarships are offered by universities, provincial governments, and external organizations.
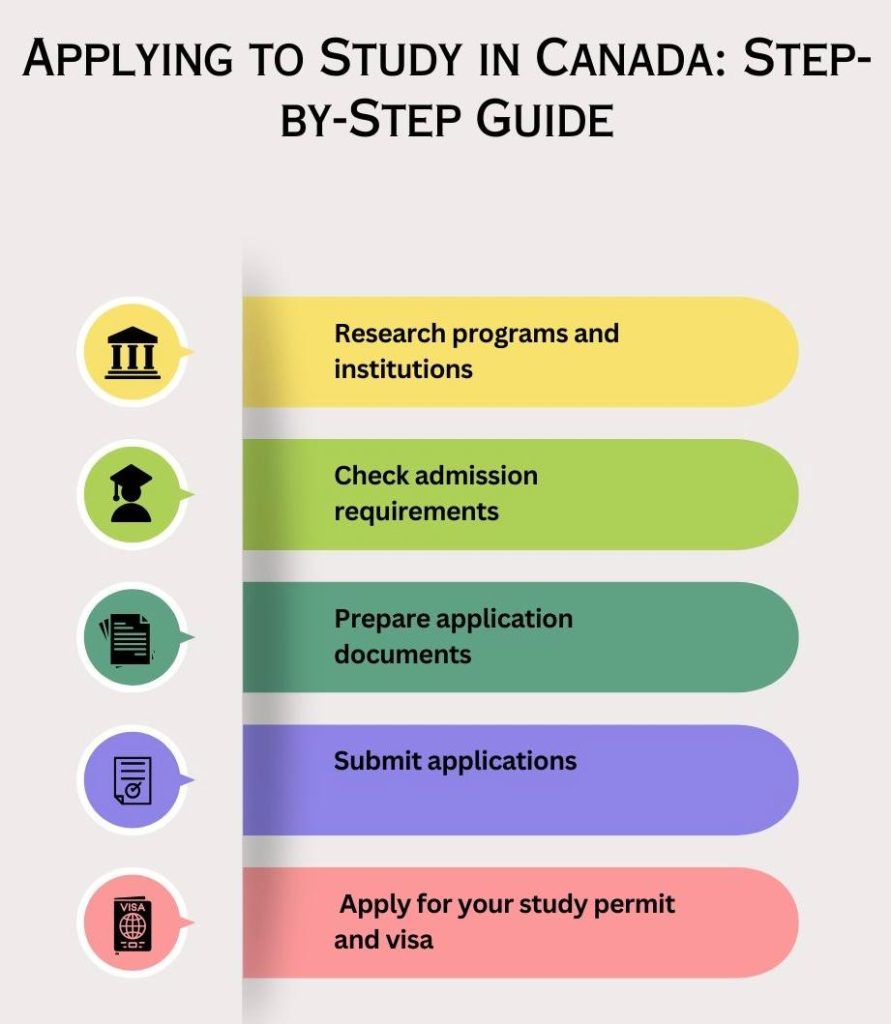
Applying to Study in Canada: Step-by-Step Guide
Once you’ve chosen your program and institution, here’s how to move forward:
- Research programs and institutions that align with your goals.
- Check admission requirements for eligibility.
- Prepare application documents, including transcripts, recommendation letters, a Statement of Purpose (SOP), and language test results.
- Submit applications through the institution’s online portal.
- Once accepted, apply for your study permit and visa with all required documentation.
Research Programs and Institutions
The first step toward studying in Canada is to explore programs and universities that best match your academic and career goals. Look at factors like admission criteria, faculty expertise, research facilities, and campus resources. Don’t forget to check application deadlines and make note of requirements specific to international students in Canada.
Check Eligibility Requirements
Before submitting applications, ensure you meet the general requirements for studying in Canada. These include an acceptance letter from a Designated Learning Institution (DLI), proof of sufficient funds, and language proficiency scores (English or French, depending on your program). Some institutions may also ask for letters of recommendation, a Statement of Purpose (SOP), or other supporting documents.
Prepare Application Documents
Organise all necessary paperwork in advance. This usually includes:
- Academic transcripts and certificates
- Proof of English or French proficiency (IELTS, TOEFL, etc.)
- Recommendation letters
- A strong Statement of Purpose (SOP)
- The newly required Provincial Attestation Letter
Carefully review each institution’s guidelines to avoid delays or rejections.
Submit Applications
Once ready, apply to your chosen institutions before the deadlines. Most Canadian colleges and universities allow online applications, making the process simple and accessible. Be sure to include all required documents and pay any application fees..
Apply for Study Permit and Visa
After receiving an acceptance letter from a DLI, the next step is to apply for your study permit (and visa, if applicable). Applications are submitted through Immigration, Refugees and Citizenship Canada (IRCC). You’ll need to provide documents such as your acceptance letter, proof of funds, and any additional documents requested by IRCC.
Preparing for Arrival
Managing finances is a key part of preparing to study abroad. You should budget for:
- Tuition fees
- Living expenses (housing, food, daily costs)
- Books and supplies
Look into scholarships in Canada, bursaries, and part-time job opportunities to help cover costs. Also, make sure you have health insurance. Some provinces provide public healthcare to international students, while others require private coverage
Once your study permit and visa are approved, begin planning for your move. Research the city where your university is located, arrange housing (on-campus or off-campus), and learn about Canadian culture. Many institutions have international student support services to guide you through the transition.
Cost of Living in Canada
The cost of living varies across Canada depending on the city. Here’s a breakdown:
- Tuition Fees: Average tuition for international undergraduates in 2022 was $36,100 CAD/year, significantly lower than the U.S. (average $64,386 USD). Costs differ by program and institution.
- Accommodation: Housing costs are higher in large cities like Toronto and Vancouver. For example, the University of Toronto estimates student housing costs between $1,080–$2,982 CAD/month. Shared apartments and homestays may be more affordable.
- Daily Expenses: Groceries in Toronto average $275–$325 CAD/month, compared to $200–$250 CAD/month in Montreal. Transportation costs also vary depending on the city.
Health Insurance: Coverage is mandatory. Some provinces include international students in public healthcare plans; others require private insurance, often arranged through the institution.
Post-Graduation Opportunities
The cost of living varies across Canada depending on the city. Here’s a breakdown:
- Tuition Fees: Average tuition for international undergraduates in 2022 was $36,100 CAD/year, significantly lower than the U.S. (average $64,386 USD). Costs differ by program and institution.
- Accommodation: Housing costs are higher in large cities like Toronto and Vancouver. For example, the University of Toronto estimates student housing costs between $1,080–$2,982 CAD/month. Shared apartments and homestays may be more affordable.
- Daily Expenses: Groceries in Toronto average $275–$325 CAD/month, compared to $200–$250 CAD/month in Montreal. Transportation costs also vary depending on the city.
- Health Insurance: Coverage is mandatory. Some provinces include international students in public healthcare plans; others require private insurance, often arranged through the institution.
Post-Graduation Work Permit (PGWP)
After completing studies, graduates may apply for a PGWP, which allows them to work in Canada for up to three years (depending on program length). The PGWP provides valuable work experience and is a major stepping stone to permanent residency.
Permanent Residency (PR)
Canada offers several PR pathways for international students, including the Canadian Experience Class (CEC), Federal Skilled Worker Program (FSWP), Provincial Nominee Programs (PNPs), the Atlantic Immigration Program, and the Rural and Northern Immigration Pilot. Work experience gained during your PGWP greatly improves eligibility.
Scholarships and Funding
In addition to support during studies, many Canadian institutions and organisations offer scholarships for international graduates. These can fund advanced education, research, or entrepreneurial projects.

Key Updates for International Students in 2025
The Canadian government introduced new rules through IRCC to improve fairness and align student pathways with labor market needs.
- Revised PGWP Eligibility
- University Graduates (Bachelor’s, Master’s, PhD): Minimum CLB 7 (English) or NCLC 7 (French). All fields are eligible.
- College Graduates & Other Programs: Minimum CLB 5/NCLC 5. Eligible fields include STEM, healthcare, trades, transportation, and agriculture.
- University Graduates (Bachelor’s, Master’s, PhD): Minimum CLB 7 (English) or NCLC 7 (French). All fields are eligible.
- Off-Campus Work Hours
Students may now work 24 hours per week (previously 20). - End of Flagpoling for PGWP Applications
Applications must now be submitted online within Canada. - Student Direct Stream (SDS) Discontinued
SDS and Nigeria Student Express were ended to create a fairer process. - Spousal Open Work Permits
Only spouses of students in graduate and professional programs are eligible. - Study Permit at Ports of Entry
Applications must be submitted online; they are no longer available at entry points.
Canada’s 2025 Study Permit Application Cap
To manage growing numbers, Canada has set a cap of 505,162 applications for 2025 (Jan 22 – Dec 31). This applies to applications accepted for processing—not permits issued.
- Applications require a Provincial/Territorial Attestation Letter.
- Provinces will manage a share of applications to align with housing and labour market capacity.
- Applications beyond the cap will be refunded but not processed.
Tip: Apply early and prepare all required documents well in advance.
How to Apply to Canadian Universities
Each university sets its own admission requirements, but most expect:
- Proof of English or French proficiency (IELTS, TOEFL, PTE, or TEF).
- Application fees ranging from $50–$150 CAD.Required documents such as: transcripts, diplomas, passport copy, resume, recommendation letters, SOP, and proof of funds. Some programs may also require portfolios or writing samples.
Application Timeline:
- Fall intake (Sept): Deadlines usually Jan–Feb.
- Winter intake (Jan): Deadlines usually Nov–Dec.
Apply 8–12 months in advance to secure your spot.
Conclusion
Studying in Canada offers international students access to a world-class education system, a safe and inclusive environment, and clear post-graduation opportunities. With proper research, financial planning, and timely applications, you can begin an exciting journey toward academic success and a bright future in Canada.



